Search Results for: light energy
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Light energy
Definition noun A form of energy consisting of particle-like photons with wavelike properties, and in which affects the... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
photobiology
Photobiology Definition Photobiology, the biology of light, is a subdiscipline in biology. It focuses on the effects of... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
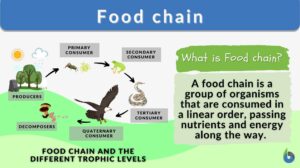
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
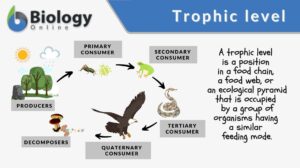
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis Definition Biosynthesis refers to the production (synthesis) of a complex chemical compound from simpler... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Accessory pigment
Definition noun, plural: accessory pigments A non-chlorophyll pigment inside the chloroplast of photosynthetic organisms,... Read More
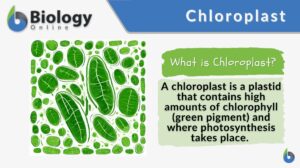
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
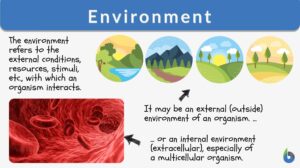
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More